Can You Get Skin Cancer From Drawing On Yourself
Skin Cancer Overview
Peel cancer is the about mutual of all human cancers. In 2022, well-nigh 100,000 people in the U.S. are expected to be diagnosed with some type of the disease. Near 7,650 are expected to die.
Cancer occurs when normal cells undergo a transformation and abound and multiply without normal controls. Here are the cancer basics:
- As the cells multiply, they form a mass called a tumor.
- Tumors are cancerous only if they are malignant. This means that they encroach on and invade neighboring tissues (specially lymph nodes) considering of their uncontrolled growth.
- Tumors may also travel to remote organs via the bloodstream. This procedure of invading and spreading to other organs is chosen metastasis.
- Tumors overwhelm surrounding tissues by invading their infinite and taking the oxygen and nutrients they need to survive and function.
At that place are iii major types of skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma. The first 2 skin cancers are grouped together every bit not-melanoma skin cancers. Other unusual types of skin cancer include Merkel prison cell tumors and dermatofibrosarcoma protruberans.
Here are the basics on skin cancers:
- The vast majority of peel cancers are basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. While malignant, these are unlikely to spread to other parts of the body if treated early. They may be locally disfiguring if non treated early.
- A pocket-size but pregnant number of skin cancers are malignant melanomas. Malignant melanoma is a highly aggressive cancer that tends to spread to other parts of the torso. These cancers may exist fatal if not treated early on.
Like many cancers, skin cancers start every bit precancerous lesions. These precancerous lesions are changes in peel that are not cancer, but could get cancer over time. Medical professionals oft refer to these changes as dysplasia. Some specific dysplastic changes that occur in pare are every bit follows:
- Actinic keratosis is an area of ruby-red or brown, scaly, rough skin, which tin can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
A nevus is a mole, and abnormal moles are chosen dysplastic nevi. These can potentially develop into melanoma over time. - Moles are simply growths on the skin that rarely develop into cancer. Most people take 10 to 30 moles on their trunk that tin can be identified as flat or raised, smoothen on the surface, circular or oval in shape, pink, tan, brown or skin-colored, and no larger than a quarter-inch across. If a mole on your body looks different from the others, inquire your health intendance provider to take a look at information technology.
- Dysplastic nevi, or abnormal moles, are non cancer, but they tin can become cancer. People sometimes have every bit many as 100 or more dysplastic nevi, which are ordinarily irregular in shape, with notched or fading borders. Some may be flat or raised, and the surface may be smooth or rough ("pebbly"). They are often big, at a quarter-inch across or larger, and are typically of mixed color, including pink, scarlet, tan, and brown.
Recent studies show the number of skin cancer cases in the U.S. growing at an alarming rate. Fortunately, increased sensation on the part of Americans and their health care providers has resulted in earlier diagnosis and improved outcomes.
Continued
Skin Cancer Causes
Ultraviolet (UV) low-cal exposure, about normally from sunlight, is overwhelmingly the about frequent crusade of skin cancer.
Other important causes of skin cancer include the post-obit:
- Apply of tanning booths
- Immunosuppression, or impairment of the immune arrangement
- Exposure to unusually high levels of radiations, such equally from X-rays
- Contact with certain chemicals, such as arsenic (miners, sheep shearers, and farmers) and hydrocarbons in tar, oils, and soot (which may crusade squamous cell carcinoma)
The following people are at the greatest risk of skin cancer:
- People with fair skin, especially types that freckle, sunburn easily, or go painful in the lord's day
- People with calorie-free (blond or scarlet) hair and bluish or green eyes
- Those with certain genetic disorders that deplete skin paint , such as albinism and xeroderma pigmentosum (a disease in which Deoxyribonucleic acid repair mechanisms, especially in response to ultraviolet light, is impaired)
- People who have already been treated for skin cancer
- People with numerous moles, unusual moles, or large moles that were present at birth
- People with close family members who accept developed skin cancer
- People who had at to the lowest degree ane severe sunburn early in life
- People with burns unrelated to sunburn
- People with indoor occupations and outdoor recreational habits
Basal cell carcinomas and squamous prison cell carcinomas are more common in older people. Melanomas are one of the well-nigh common cancers in younger people, especially in people ages 25 to 29. The adventure of melanoma rises with historic period.
Skin Cancer Symptoms
Skin cancer symptoms depend on the type of skin cancer that has developed.
A basal cell carcinoma (BCC) usually looks like a raised, smooth, pearly bump on the lord's day-exposed skin of the head, neck, or shoulders. Others signs include:
- Small-scale claret vessels may be visible within the tumor.
- A central low with crusting and bleeding (ulceration) oftentimes develops.
- A BCC often appears every bit a sore that does not heal.
A squamous jail cell carcinoma (SCC) is normally a well-divers, red, scaling, thickened bump on sun-exposed skin. It may ulcerate and bleed, and left untreated, may develop into a large mass.
The majority of malignant or cancerous melanomas are brownish-to-black pigmented lesions. Other signs of a cancerous melanoma include:
- A change in size, shape, color, or peak of a mole
- The appearance of a new mole during adulthood, or new pain, itching, ulceration, or bleeding of an existing mole
Continued
The following easy-to-remember guideline, "ABCDE," is useful for identifying malignant melanoma:
- Asymmetry -- 1 side of the lesion does not look similar the other.
- Border irregularity -- Margins may be notched or irregular.
- Color -- Melanomas are often a mixture of black, tan, brown, blueish, red, or white.
- Diameter -- Cancerous lesions can be larger than half dozen mm across (about the size of a pencil eraser), although with early on detection they will not reach this size.
- Evolution -- has a mole inverse over time?
When to Seek Medical Care for Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or take had extensive lord's day exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your master wellness care provider or a dermatologist check whatever moles or spots that concern y'all.
Run into your health intendance provider to bank check your skin if you lot notice whatsoever changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas (such as darker or a change in areas of skin or moles).
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist (dermatologist) or cancer specialist (oncologist) will talk to you nigh symptoms of metastatic disease that might require intendance in a hospital.
Exams and Tests for Skin Cancer
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider volition probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist volition examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are idea to be peel cancer, may then be checked. Tests for pare cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to browse the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a estimator program evaluates images of the lesion to point if it's cancerous.
- A sample of peel (biopsy) volition exist taken and so that the suspicious area of peel can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is washed in the dermatologist'southward office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo farther testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest 10-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
Pare Cancer Handling
Skin cancer handling for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is straightforward. Usually, surgical removal of the lesion is adequate. Malignant melanoma, yet, may require several treatment methods -- depending on the size of the tumor -- including surgery, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy. Considering of the complexity of handling decisions, people with malignant melanoma may benefit from the combined expertise of the dermatologist, a cancer surgeon, and an oncologist.
Peel Cancer Intendance at Home
Home treatment is not advisable for pare cancer. These conditions require the care of a dermatologist or specialist in skin cancers.
Exist agile in preventing and detecting skin cancer on yourself and others. Perform regular self-examinations of your skin and note whatever changes.
Medical Treatment for Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more data, see Surgery.
People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the employ of a small beam of radiations targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy tin crusade irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It tin also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of sure low-chance nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side furnishings include musculus spasms, hair loss, gustatory modality changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work amend than existing therapies.
Surgery for Skin Cancer
Pocket-size skin cancer lesions may exist removed through a variety of techniques, including elementary excision (cut information technology away), electrodesiccation and curettage (scraping the tumor and then burning the tissue with an electrical needle), and cryosurgery (freezing the expanse with liquid nitrogen).
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, one-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is besides removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may too be removed and tested for cancer. The lookout lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to place which lymph nodes are nearly likely to be affected.
Connected
After Skin Cancer Handling
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist'south part. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within iii years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you lot suspect a problem.
If y'all accept advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include full body peel exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest Ten-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals betwixt follow-up appointments will increment. Eventually these checks may be done only one time a year.
Skin Cancer Prevention
You can reduce your chance of getting pare cancer past post-obit these guidelines:
- Limit sun exposure. Attempt to avert the sun's intense rays between 10 a.k. and four p.grand.
- Apply sunscreen every day. Use a sunscreen with dominicus protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 both before and every 60 to 80 minutes during outdoor exposure. Select products that filter both UVA and UVB light. The label will tell yous.
- If you are likely to sunburn, wear a long-sleeved shirt, pants and a wide-brimmed hat.
- Avoid artificial tanning booths.
- Bear monthly self-exams.
Skin Self-Exams
Monthly peel cocky-exams improve your chances of finding a skin cancer early, when it has done a minimum of damage to your pare and can exist treated easily. Regular cocky-exams help you recognize any new or irresolute features.
- The best time to practice a self-exam is right after a shower or bathroom.
- Do the self-examination in a bright room; use a full-length mirror and a manus-held mirror.
- Learn where your moles, birthmarks, and blemishes are, and what they look like.
- Each time yous do a self-exam, check these areas for changes in size, texture, and color, and for ulceration. If you observe any changes, phone call your primary care provider or dermatologist.
Check all areas of your torso, including "hard-to-reach" areas. Enquire a loved ane to assist you check if there are areas you lot can't see.
- Await in the full-length mirror at your forepart and your back (utilize the hand-held mirror to exercise this). Raise your arms and look at your left and right sides.
- Curve your elbows and look carefully at your palms, nails, forearms (front and back), and upper arms.
- Examine the backs and fronts of your legs. Look at your buttocks (including the area between the buttocks) and your genitals (use the paw-held mirror to brand sure yous come across all skin areas).
- Sit down and examine your feet carefully, including the nails, soles and betwixt the toes.
- Await at your scalp, face, and neck. You may use a rummage or blow dryer to move your hair while examining your scalp. Y'all may also enlist the assist of a friend or family unit member.
If you are at loftier take a chance for developing peel cancer, enquire you doctor well-nigh oral nicotinamide, a vitamin B3 supplement taken twice daily in pill grade that tin decrease the charge per unit of new squamous prison cell and basal cells by nearly 25%.
Continued
Skin Cancer Outlook
Although the number of peel cancers in the U.S. continues to rise, more peel cancers are being caught before, when they are easier to treat. Thus, illness and death rates have decreased.
When treated properly, the cure rate for both basal prison cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) approaches 95%. The remaining cancers recur at some indicate afterward treatment.
- Recurrences of these cancers are almost ever local (not spread elsewhere in the body), but they often crusade pregnant tissue destruction.
- 2% of squamous cell carcinomas will somewhen spread elsewhere in the trunk and turn into unsafe cancer. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually seen in people with compromised allowed systems.
In most cases, the outcome of cancerous melanoma depends on the thickness of the tumor at the time of treatment.
- Sparse lesions are about always cured by simple surgery lonely.
- Thicker tumors, which ordinarily have been nowadays for some fourth dimension simply have gone undetected, may spread to other organs. Surgery removes the tumor and whatsoever local spread, but it cannot remove distant metastasis. Other therapies, such every bit radiation therapy, immunotherapy or chemotherapy, are used to treat the metastatic tumors.
- Malignant melanoma causes more than 75% of deaths from skin cancer.
Pare Cancer Support Groups and Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you lot and for your family and friends. You lot volition probably have many worries nearly how the cancer will affect yous and your ability to "live a normal life," that is, to treat your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel broken-hearted and depressed. Some people experience angry and resentful; others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking nearly their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer back up until they run across how you lot are coping. Don't wait for them to bring information technology upwardly. If you want to talk almost your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people don't want to "burden" their loved ones, or prefer talking nearly their concerns with a more than neutral professional. A social worker, advisor, or fellow member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped past talking to other people who accept cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the aforementioned affair tin can be remarkably reassuring. Back up groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Order too has data about support groups throughout the U.Southward.
For More Information Near Skin Cancer
National Cancer Plant, Cancer Data Service (CIS)
Toll-gratis: (800) 4-CANCER (800) 422-6237
TTY (for deaf and difficult of hearing callers): (800) 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
255 Lexington Artery, 11th Floor
New York, NY 10016
(212)754-5176
world wide web.skincancer.org
Skin Cancer Web Links
For information almost clinical trials in skin cancer treatment, visit the National Institute of Health's Clinical Trials database. For other valuable information, visit the post-obit websites:
American Academy of Dermatology
American Cancer Society
National Cancer Institute
Pare Cancer Pictures
Media file one: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
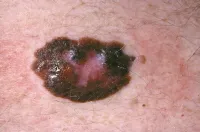
Media file two: Skin cancer. Basal prison cell carcinoma.
Media file iii: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, Doc, Managing director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Intendance Organization.
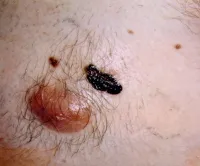
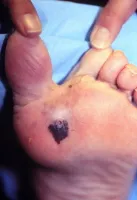
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan One thousand. Swetter, Physician, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Dispensary, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Wellness Care System.
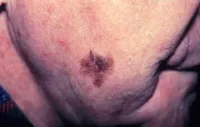
Media file 5: Peel cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Dispensary, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care Organization.
Continued
Media file 6: Peel cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma (pare cancer) on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.

Source: https://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/melanoma-guide/skin-cancer
Posted by: larsonsuat1947.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can You Get Skin Cancer From Drawing On Yourself"
Post a Comment